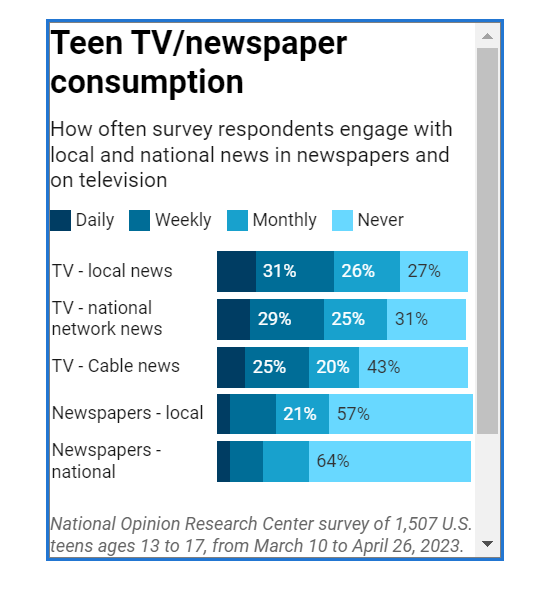
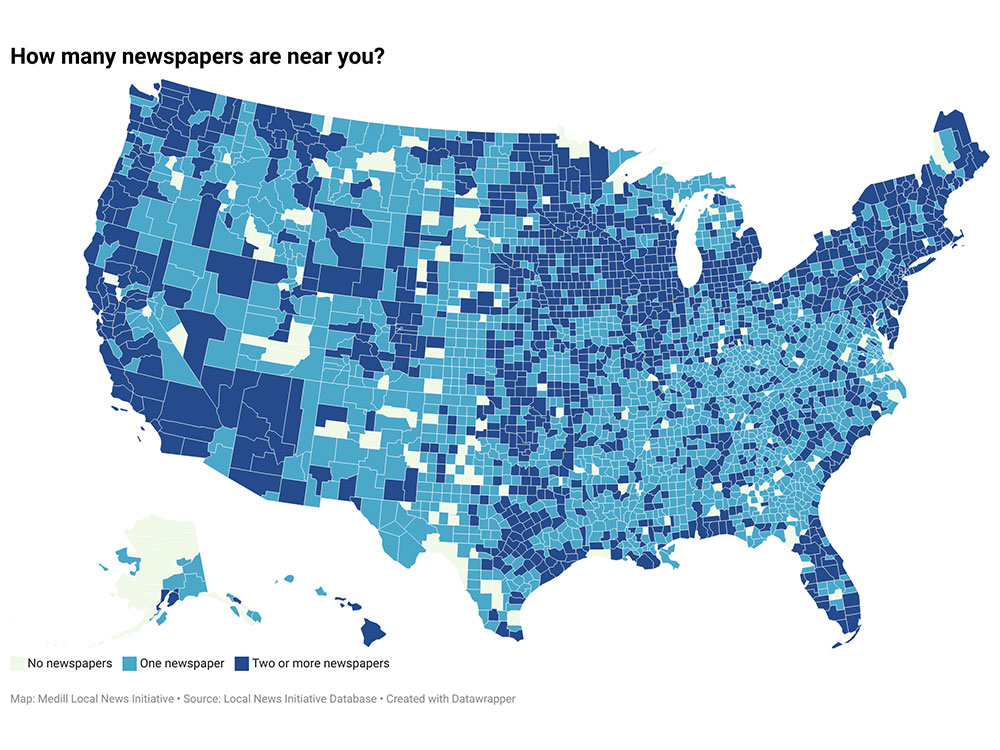
The number of local news deserts in the U.S. jumped to record levels this year as newspaper closures continued unabated, and funding cuts to public radio could worsen the problem in coming months, according to the Medill State of Local News Report 2025 released today.
While the local news crisis deepened overall, Medill researchers found cause for optimism — more than 300 local news startups have launched over the past five years, 80% of which were digital-only outlets.
For the fourth consecutive year, the Medill Local News Initiative conducted a months-long, county-by-county survey of local news organizations to identify trends in the rapidly morphing local media landscape. Researchers looked at local newspapers, digital-only sites, ethnic media and public broadcasters.
This year’s report also includes an analysis of a timely issue: the potential impact of the federal defunding of public broadcasting on local news deserts. And for the first time, Medill researchers examined the decline in digital readership at newspapers.
Key findings from the Medill study:
The number of news desert counties rose to 213 in 2025, a jump from 206 in last year’s report. In another 1,524 counties, there’s only one remaining news source. Taken together, some 50 million Americans have limited to no access to local news. Twenty years ago, there were about 150 news desert counties, with about 37 million Americans at the time living in news deserts.
The rise in news deserts was accompanied by an increase in newspaper closures, which ticked up to 136 this past year, a rate of more than two per week. Medill tracked 130 in last year’s report.
In a marked departure, most of this year’s closures came at smaller, independently owned newspapers — not those controlled by large chains — signaling that an increasing number of long-time family publishers are surrendering to economic pressures.
Total jobs at newspapers slumped 7% in the past year. The industry has now lost more than three-quarters of its jobs since 2005.
More than 200 newspapers changed hands in the past year, down from the number of transactions last year but still a torrid pace by historical standards.
Nearly 300 public radio stations and more than 100 public television stations are producing local reporting. In nine counties, public radio is the sole news source, making those areas especially vulnerable to becoming news deserts in coming months.
Utilizing predictive modeling created by the school’s Spiegel Research Center, the Medill team found 250 counties at high risk of becoming news deserts over the next decade.
Web traffic to 100 of the largest newspapers has plummeted more than 45% in the past four years, according to a Medill analysis of data tracked by the media analytics company Comscore.
The report counted more than 300 local news startups in the past five years across virtually every state, demonstrating a surge of entrepreneurship that has come along with a wave of philanthropic support. The vast majority of those startups, however, are in metro areas, leaving rural and less affluent areas further behind.
The number of local news sites that are part of larger national networks is continuing to multiply. This year, there are 849 sites across 54 separate networks, up 14% from the 742 individual sites across 23 networks. This growth illustrates the increasingly prominent role of digital network sites on the local news landscape.
“This report highlights the historic transformation in local news,” said Tim Franklin, professor and John M. Mutz Chair in Local News at Medill. “On one hand, news deserts are expanding, and closures are continuing apace. On the other, hundreds of startups are emerging. The questions are what will the local news ecosystem look like in a few years, and will parts of the U.S. be left behind?”
Zach Metzger, director of the Medill State of Local News Project, said, “Over the past two decades, we’ve seen a dramatic reshaping in local news. Unlike in previous years, however, the majority of papers shutting down now are smaller, family-owned enterprises. These are often the most trusted active local news sources, and their loss creates new challenges for local news access in many communities.”
The Medill State of Local News Project is funded by grants and gifts from the Knight Foundation, MacArthur Foundation, Joyce Foundation, Microsoft, the Southern Newspaper Publishers Foundation, the Myrta J. Pulliam Charitable Trust and Medill alumni John M. Mutz and Mark Ferguson.